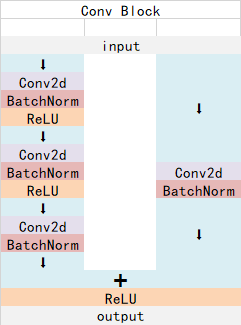
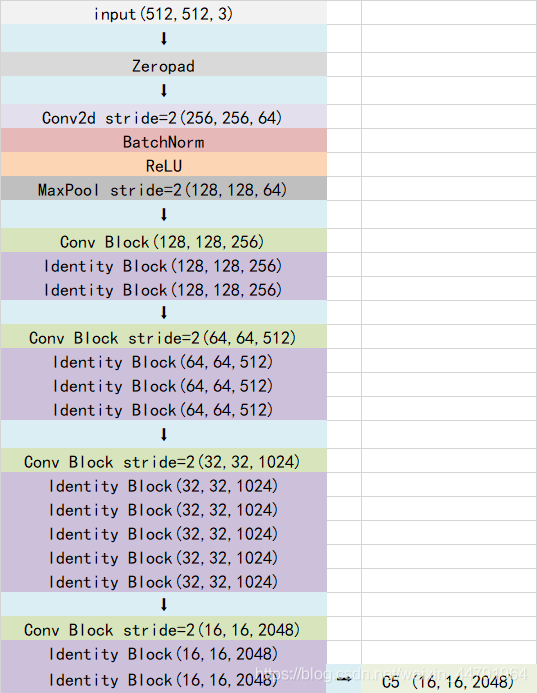
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
|
class Generator(object):
def __init__(self,batch_size,train_lines,val_lines,
input_size,num_classes,max_objects=100):
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.train_lines = train_lines
self.val_lines = val_lines
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = (int(input_size[0]/4) , int(input_size[1]/4))
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.max_objects = max_objects
def get_random_data(self, annotation_line, input_shape, random=True, jitter=.3, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5, proc_img=True):
'''r实时数据增强的随机预处理'''
line = annotation_line.split()
image = Image.open(line[0])
iw, ih = image.size
h, w = input_shape
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line[1:]])
# resize image
new_ar = w/h * rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)/rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
scale = rand(0.25, 2)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# place image
dx = int(rand(0, w-nw))
dy = int(rand(0, h-nh))
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image = new_image
# flip image or not
flip = rand()<.5
if flip: image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
# distort image
hue = rand(-hue, hue)
sat = rand(1, sat) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, sat)
val = rand(1, val) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, val)
x = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(image,np.float32)/255, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
x[..., 0] += hue*360
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x[:,:, 0]>360, 0] = 360
x[:, :, 1:][x[:, :, 1:]>1] = 1
x[x<0] = 0
image_data = cv2.cvtColor(x, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)*255
# correct boxes
box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
if flip: box[:, [0,2]] = w - box[:, [2,0]]
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)] # discard invalid box
box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))
box_data[:len(box)] = box
if len(box) == 0:
return image_data, []
if (box_data[:,:4]>0).any():
return image_data, box_data
else:
return image_data, []
def generate(self, train=True):
while True:
if train:
# 打乱
shuffle(self.train_lines)
lines = self.train_lines
else:
shuffle(self.val_lines)
lines = self.val_lines
batch_images = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.input_size[0], self.input_size[1], self.input_size[2]), dtype=np.float32)
batch_hms = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.output_size[0], self.output_size[1], self.num_classes), dtype=np.float32)
batch_whs = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects, 2), dtype=np.float32)
batch_regs = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects, 2), dtype=np.float32)
batch_reg_masks = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects), dtype=np.float32)
batch_indices = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects), dtype=np.float32)
b = 0
for annotation_line in lines:
img,y=self.get_random_data(annotation_line,self.input_size[0:2])
if len(y)!=0:
boxes = np.array(y[:,:4],dtype=np.float32)
boxes[:,0] = boxes[:,0]/self.input_size[1]*self.output_size[1]
boxes[:,1] = boxes[:,1]/self.input_size[0]*self.output_size[0]
boxes[:,2] = boxes[:,2]/self.input_size[1]*self.output_size[1]
boxes[:,3] = boxes[:,3]/self.input_size[0]*self.output_size[0]
for i in range(len(y)):
bbox = boxes[i].copy()
bbox = np.array(bbox)
bbox[[0, 2]] = np.clip(bbox[[0, 2]], 0, self.output_size[1] - 1)
bbox[[1, 3]] = np.clip(bbox[[1, 3]], 0, self.output_size[0] - 1)
cls_id = int(y[i,-1])
h, w = bbox[3] - bbox[1], bbox[2] - bbox[0]
if h > 0 and w > 0:
ct = np.array([(bbox[0] + bbox[2]) / 2, (bbox[1] + bbox[3]) / 2], dtype=np.float32)
ct_int = ct.astype(np.int32)
# 获得热力图
radius = gaussian_radius((math.ceil(h), math.ceil(w)))
radius = max(0, int(radius))
batch_hms[b, :, :, cls_id] = draw_gaussian(batch_hms[b, :, :, cls_id], ct_int, radius)
batch_whs[b, i] = 1. * w, 1. * h
# 计算中心偏移量
batch_regs[b, i] = ct - ct_int
# 将对应的mask设置为1,用于排除多余的0
batch_reg_masks[b, i] = 1
# 表示第ct_int[1]行的第ct_int[0]个。
batch_indices[b, i] = ct_int[1] * self.output_size[0] + ct_int[0]
batch_images[b] = preprocess_image(img)
b = b + 1
if b == self.batch_size:
b = 0
yield [batch_images, batch_hms, batch_whs, batch_regs, batch_reg_masks, batch_indices], np.zeros((self.batch_size,))
batch_images = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.input_size[0], self.input_size[1], 3), dtype=np.float32)
batch_hms = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.output_size[0], self.output_size[1], self.num_classes),
dtype=np.float32)
batch_whs = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects, 2), dtype=np.float32)
batch_regs = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects, 2), dtype=np.float32)
batch_reg_masks = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects), dtype=np.float32)
batch_indices = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.max_objects), dtype=np.float32)
|